108 Glen Osmond Road, Parkside
What is SIBO (Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth)?
SIBO occurs when there is an abnormal increase in the population of bacteria in the small intestine, particularly types of bacteria usually found in other parts of the gut, such as the colon. This bacterial overgrowth can disrupt digestion, nutrient absorption, and gut health.
Types of SIBO
Hydrogen-Dominant SIBO
Hydrogen Sulphide-Dominant SIBO
Symptoms of SIBO
Digestive Issues:
Bloating and abdominal distension.
Gas (flatulence or belching).
Diarrhea or constipation, depending on the type.
Stomach pain or cramping.
Nutritional Deficiencies:
Unintended weight loss.
Malabsorption of vitamins (e.g., B12, fat-soluble vitamins).
Fatty stools (steatorrhea).
Systemic Symptoms:
Fatigue or brain fog.
Joint pain.
Skin issues like rosacea or eczema.
Food intolerances (e.g., lactose or fructose intolerance).
Causes of SIBO
Impaired Gut Motility:
Sluggish peristalsis allows bacteria to overgrow.
Conditions like IBS, diabetes, or hypothyroidism.
Structural Abnormalities:
Surgery (e.g., gastric bypass) or anatomical issues like diverticulosis.
Low Stomach Acid:
Reduced acid production can fail to kill excess bacteria.
Immune Deficiencies:
Weak immune function can lead to bacterial imbalance.
Medications:
Long-term use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or antibiotics.
Dietary Triggers:
High carbohydrate or refined sugar intake fuels bacterial fermentation.
SIBO Testing:
Testing for Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
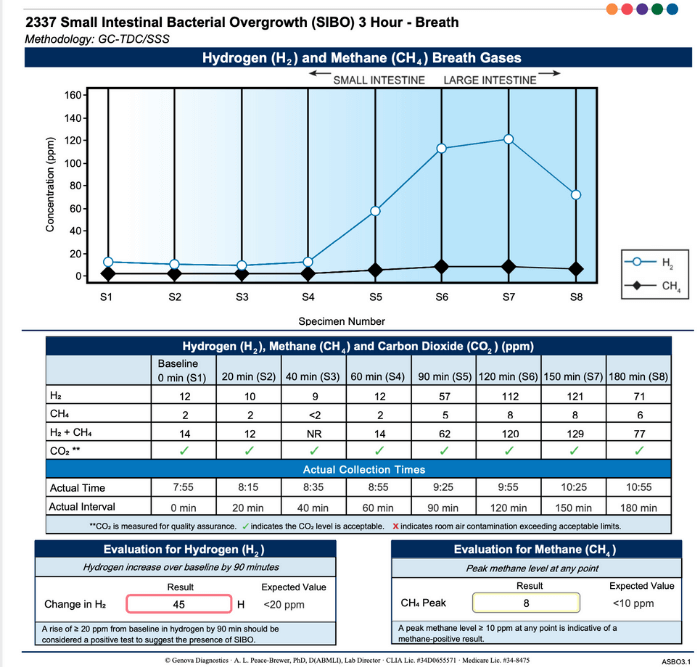
Hydrogen-Methane Breath Test
This is the most common and non-invasive test for diagnosing SIBO.
How it Works:
The patient drinks a sugar solution (commonly lactulose or glucose).
Bacteria in the small intestine ferment the sugar, producing gases (hydrogen and methane) that are absorbed into the bloodstream and exhaled through the lungs.
The patient's breath is measured at regular intervals to track gas production.
What It Detects:
Hydrogen gas indicates carbohydrate fermentation by bacteria, typically associated with hydrogen-dominant SIBO.
Methane gas is linked to methane-dominant SIBO, often causing constipation.
Hydrogen sulphide (in some advanced tests) is linked to hydrogen sulfide-dominant SIBO, associated with diarrhea or alternating symptoms.
Correct Diet for SIBO

A proper diet helps starve the overgrown bacteria while nourishing the patient. The most effective approaches include:
Low FODMAP Diet
FODMAPs are fermentable carbs that feed bacteria. Avoid foods like:
High-FODMAP Foods: Garlic, onions, beans, lentils, broccoli, cauliflower, apples, wheat, dairy (lactose).
Safe Foods: Zucchini, spinach, cucumber, blueberries, gluten-free grains, and lactose-free dairy.
Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD)
Focuses on monosaccharides (single sugars) for easier digestion. Avoid complex carbs like grains and starches.
Elemental Diet
A liquid formula with pre-digested nutrients (amino acids, simple carbs, healthy fats) that bypasses the small intestine, starving the bacteria.
Naturopathic and Ayurvedic Herbal Treatments for SIBO
1. Herbal Antibiotics (Naturopathy)
These can help reduce bacterial overgrowth:
Berberine: Found in herbs like barberry and goldenseal, effective against both hydrogen- and methane-producing bacteria.
Neem: Antibacterial properties target harmful bacteria.
Oregano Oil: Potent antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Allicin: Extracted from garlic, particularly useful for methane-dominant SIBO.
Grapefruit Seed Extract: Broad-spectrum antimicrobial.
2. Ayurvedic Treatments
Triphala: Balances digestion and regulates gut motility.
Turmeric (Curcumin): Anti-inflammatory and healing for the gut lining.
Ajwain (Carom Seeds): Aids digestion and reduces bloating.
Hing (Asafoetida): Combats gas and abdominal discomfort.
Cumin, Coriander, and Fennel Seeds: Soothe the digestive tract and reduce bloating.
3. Gut Healing and Detoxifying Herbs
Slippery Elm: Coats and soothes the gut lining.
Aloe Vera: Reduces inflammation and promotes gut healing.
Licorice Root (DGL): Protects the gut lining and alleviates discomfort.
4. Probiotics
Use cautiously, as certain strains (e.g., Saccharomyces boulardii) can help rebalance gut flora but may worsen symptoms in methane-dominant SIBO.
Lifestyle Recommendations
Improve Gut Motility:
Incorporate natural motility agents like ginger or Triphala.
Avoid snacking between meals to allow the migrating motor complex (MMC) to clear the gut.
Stress Management:
High stress affects digestion, so practice yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
Sleep:
Aim for 7–8 hours of quality sleep to support gut repair and overall health.
Treating SIBO requires a multifaceted approach involving dietary changes, herbal remedies, and lifestyle modifications. Ayurvedic and naturopathic solutions like Triphala, turmeric, neem, and oregano oil offer effective natural alternatives to conventional antibiotics, while a low-FODMAP or SCD diet helps starve overgrown bacteria. If symptoms persist, consulting a qualified practitioner for personalized treatment is crucial. CONTACT
Disclaimer : Sandeep Kumar and Anupam Vasudeva are not GP, they have Ayurveda medical degree from India where it is considered equal to any other medical degree. This qualification is recognized in Australia by vetassess governing body as Complementary Health Therapists. Life Line Ayurvedic Herbal Clinic does not claim to cure a disease or terminal illness and does not create any unreasonable expectation of beneficial treatment. Ayurvedic medicines and treatments are generally considered to be safe but rarely may be associated with possible adverse reactions in individual cases. We recommend seeking urgent medical attention in the case of an adverse reaction. This website provides you with information. You must contact your Ayurvedic or another health professional before you apply them. Read More