What is Motor Neuron Disease MND:-
Motor neuron disease (MND) is a rapidly progressing neurological disorder that attacks the nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. Motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord send electrical messages from the brain to the muscles to move the arms, legs, trunk, neck, and head. As motor neurons degenerate, the muscles do not work properly and gradually weaken and waste away. This muscle weakness and wasting affects speech, swallowing, movement, and breathing.

Types of MND:-
There are various subtypes of MND. In each type, symptoms tend to start in different ways. However, as the disease progresses, the symptoms of each type of MND tend to overlap. This means that symptoms in the later stages of each type of MND become similar. The main types of MND are:
* Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). This is the classical MND and the most common type. About 8 in 10 people with MND have this type. Symptoms tend to start in the hands and feet. The muscles tend to become stiff as well as weak at first.

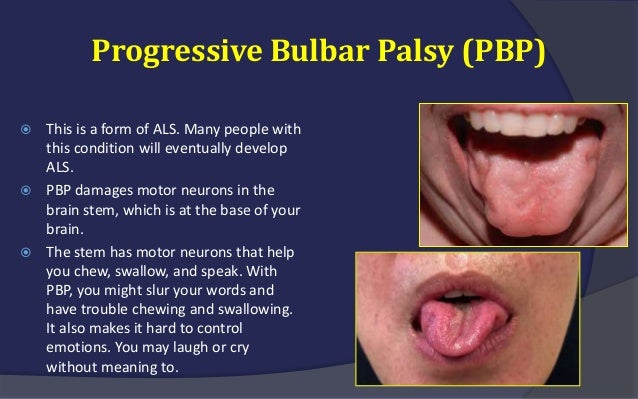
* Progressive bulbar palsy (PBP). About 2 in 10 people with MND have this type. The muscles first affected are those used for talking, chewing, and swallowing (the bulbar muscles).
* Progressive muscular atrophy (PMA). This is an uncommon form of MND. The small muscles of the hands and feet are usually first affected but the muscles are not stiff.
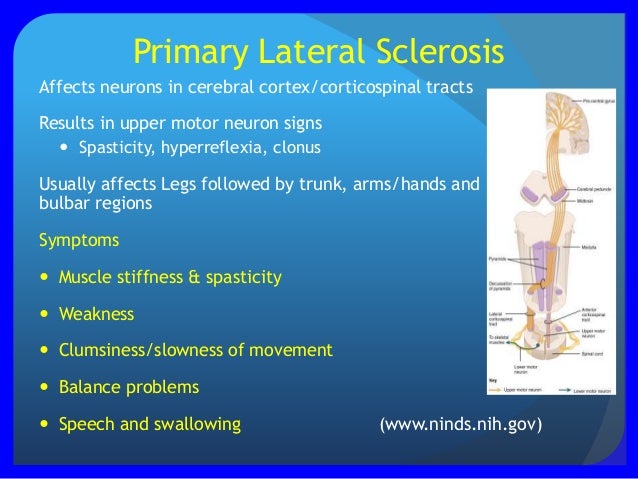
* Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS). This is a rare type of MND. It mainly causes weakness in the leg muscles. Some people with this type may also develop clumsiness in their hands or develop speech problems.
 What causes MND:-
The causes of MND are currently unclear but the generally accepted view is that this disease is a result of a combination of environmental, lifestyle and subtle genetic risks. About 5-10% of MND patients have a known family history of MND. The remaining cases (90-95%) are sporadic.
Motor neuron disease is most commonly diagnosed in those over the age of 40 years, occurring mainly in those aged between 50 and 70 years. In some cases, though, symptoms can first appear in a person's 20s.
Usually the onset of motor neurone disease is gradual but younger patients may show a more rapid progression. The average life expectancy is 2–4 years from diagnosis but some people succumb within a matter of months, while others live up to 20 years or (in rare cases) beyond.
Ayurvedic view of MND:-
What causes MND:-
The causes of MND are currently unclear but the generally accepted view is that this disease is a result of a combination of environmental, lifestyle and subtle genetic risks. About 5-10% of MND patients have a known family history of MND. The remaining cases (90-95%) are sporadic.
Motor neuron disease is most commonly diagnosed in those over the age of 40 years, occurring mainly in those aged between 50 and 70 years. In some cases, though, symptoms can first appear in a person's 20s.
Usually the onset of motor neurone disease is gradual but younger patients may show a more rapid progression. The average life expectancy is 2–4 years from diagnosis but some people succumb within a matter of months, while others live up to 20 years or (in rare cases) beyond.
Ayurvedic view of MND:-
 According to Ayurveda, Motor Neuron Diseases is caused by the Vitiation of Vata Roga and Kshaya Roga. Vata dosha is responsible for the respiratory, blood, lymphatic, excretory, and reproductive systems functioning. It is also responsible for the functioning of the brain. It also controls the secretion of various chemical neurotransmitters and hormones. The modification from having normality in life is due to the impediment in its sensory and motor activities by other doshas (Pitta and Kapha), or Dushyas like dhatus or Malas, thus leading to the disease. In such cases, the Vata becomes teemed by Kapha dosha, thus leading to reduced activity, faintness, and spasms. In Ayurveda, it comes into the under the class called Kashta Saadhya Vyadhi (difficult to cure).
According to Ayurveda, Motor Neuron Diseases is caused by the Vitiation of Vata Roga and Kshaya Roga. Vata dosha is responsible for the respiratory, blood, lymphatic, excretory, and reproductive systems functioning. It is also responsible for the functioning of the brain. It also controls the secretion of various chemical neurotransmitters and hormones. The modification from having normality in life is due to the impediment in its sensory and motor activities by other doshas (Pitta and Kapha), or Dushyas like dhatus or Malas, thus leading to the disease. In such cases, the Vata becomes teemed by Kapha dosha, thus leading to reduced activity, faintness, and spasms. In Ayurveda, it comes into the under the class called Kashta Saadhya Vyadhi (difficult to cure).
Ayurvedic Treatment options for MND:-

It’s always tough to handle MND and results depend upon the type of MND. In most of the cases due to lack of early diagnosis patients' nerve damaged had worsened his/ her mobility and other communication abilities. But in cases with early diagnosis, very good results can be achieved by suppressing the progression of disease and improving the quality of life.
Treatments include mild external therapies and specific head therapies along with internal medicines. Treatment course depends upon patients response to medicines.
Herbs and herbal compounds used in MND are:-
Ashawagandha:
Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) is a very revered herb of the Indian Ayurvedic system of medicine as a Rasayana (tonic). It is used for various kinds of disease processes and especially as a nervine tonic. Considering these facts many scientific studies were carried out and its adaptogenic/anti-stress activities were studied in detail. It was also found useful in neurodegenerative diseases. It has a GABA mimetic effect and was shown to promote the formation of dendrites. Ashwagandha also improves communication between nerve cells and stimulates the body's capacity to heal any nervous system damage.

Brahmi: Bacopa monnieri (Brahmi), an herbal nutraceutical is recognized for its role as a Medhya Rasayana or a nootropic agent in Ayurveda. Ayurvedic and other herbal medications have gained increased acceptance as they are found to be safer than the synthetic counterparts. The therapeutic effects of Bacopa monniera are believed to be exerted through triterpenoid saponins present in the plant extract. Bacosides are the triterpenoid saponins of prime importance. They have been shown to enhance nerve impulse transmission. The bacosides promote the repair of damaged neurons by upregulating neuronal synthesis and kinase activity. The bacosides also aid in the restoration of synaptic activity, which ultimately leads to nerve impulse transmission (Singh and Dhawan, 1997). The nerve impulse transmission plays a vital role in promoting healthy cognitive functions like attention span, focus, concentration, learning and memory. There is evidence which suggests that Bacopa, by the virtue of containing active constituents like bacosides, influences the synthesis and availability of the neurotransmitter, Serotonin; therefore, Bacopa helps to maintain neurotransmitter balance (Charles et al., 2011; Rauf et al., 2012a)

Kapikacchu: Kapikacchu (Mucuna pruriens) is a potent nervine tonic. It is a natural L-Dopa supplement that increases Dopamine levels in the body. Healthy levels of Dopamine are indispensable for smooth sensory function and mental agility. It calms the senses and relieves anxiety and stress. Increased Dopamine levels are believed to improve nerve conduction. It naturally manages movement disorders typical of neurodegenerative disorders. The drug has intense vata-pitta hara action. Excited vata manifests as rigidity, dryness, roughness, loss of function, and tingling sensation in the body. Kapikacchu grounds and stabilizes the erratic vata. It soothes the nervous system and restores vitality and vigor.

Turmeric: Turmeric (Curcuma longa) is a perennial, rhizomatous, herbaceous plant native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. It has long been used in India’s Ayurvedic medicine and is a key ingredient in curry. The active ingredient in turmeric is curcumin. Research has shown that curcumin can boost levels of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). BDNF is a type of brain hormone, which increases the growth of new neurons. Furthermore, curcumin might fight various degenerative processes in the brain and enhance memory.
Gotu kola: Native to the wetlands in Asia, gotu kola (Centella asiatica), also known as Indian or Asiatic pennywort, is considered the most rejuvenative herb in Ayurvedic medicine and is used both as a medicine and a vegetable. The name comes from Sri Lanka, where it thrives in the warm humid climate and is in high demand as a green salad vegetable. Gotu kola contains essential oils, tannins, plant sterols, amino acids, flavonoids, oligosaccharides, and triterpenoid saponins, including asiaticoside, madecassoside and madasiatic acid. It is rich in vitamins and minerals. Gotu kola supports healthy neurotransmitter function and improves cognition and memory. It also enhances brain function and protects the brain from degenerative conditions. It improves circulation to the brain, helping protect it from oxidative damage and reducing the risk of developing degenerative brain conditions. Gotu kola increases GABA in the central nervous system, so has a relaxing effect by reducing anxiety, and it supports the body’s ability to acclimatise to temporary stress, lowering cortisol levels and assisting with stress management. Gotu kola stimulates circulation, increasing collagen production and synthesis. It has positive effects on strengthening blood vessel walls.

Shilajeet: Shilajeet (Asphaltum) is known as a potent detoxifier for the brain, Shilajit has been shown to assist in the assimilation of nutrients, minerals and oxygen into the brain that support its ability to remove dangerous toxins. Shilajit has also been found to inhibit the enzyme that breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is critical for memory, concentration, and overall brain function – stress and aging can decrease levels of this important compound. Shilajit works to promote healthy levels of acetylcholine, further protecting the brain from degeneration. Shilajit helps in maintaining muscle strength & aids connective tissue adaptations.
 * Ashwagandha churna
* Ashwagandha churna
* Brihatvat chintamani ras
* Brahmi churna
* Panchagavya ghritam
* Kalyanavleha
* Shilajit tablets
* Saraswatarishtam
* Brahmarasayanam
* Shankhpushpi current
* Suvarnayukta Brahmi vatti
* Makardhwaj Vati
* Vatagajankush rasa
* Rasraj Rasa
Above mentioned herbs promote mental health and support the normal functioning of the brain and nervous system. They also help to treat pain, control tremors, and balance Pitta and Vata doshas in the body. Especially Brahmi and Ashwagandha help to promote memory, and good mental health, decrease inflammation, anxiety, and stress, stimulate the immune system, manage blood pressure, and eliminate free radicals out from the body.
Panchkarma Therapies quite effective in MND are :-

* Abhyandam
* Shirodhara
* Nasyam
* Pizichil
* Shastisali pinda swedan
* Marma Therapy
The Ayurvedic diagnosis and treatment of MND may vary from patient to patient and at different stages in same patient. It is advised to book a consultation with our practitioners to know which herbs and therapies will be best in your case of MND. CONTACT








