108 Glen Osmond Road, Parkside

Chronic Kidney failure or chronic renal failure (CRF) or chronic terminal kidney disorder is very common these days, with loss of kidney function. The alteration in kidney functions is visible in the form of swelling on the face and feet, fatigue, muscular weakness, and dry, itchy skin. Mainly the diabetes, hypertension, urinary tract obstructions, and immunological disorders are the causes of chronic renal failure. The severity of this CRF is graded from stage I to V depending on the kidney function.
Kidney Disease:-
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs. Each kidney is about the size of a fist.
Healthy kidneys function to remove extra water and wastes, help control blood pressure, keep body chemicals in balance, keep bones strong, tell your body to make red blood cells, and help children grow normally. Kidney disease occurs when the kidneys are no longer able to clean toxins and waste products from the blood and perform their functions to full capacity. This can happen all of a sudden (Acute) or over time (Chronic). Kidney disease can get worse over time and may lead to kidney failure. If less than 15 percent of your kidney is working normally, that’s considered kidney failure. You may have symptoms from the buildup of waste products and extra water in your body.
Acute Renal Failure:-
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) is the term that has recently replaced the term ARF. AKI is defined as an abrupt (within hours) decrease in kidney function, which encompasses both injury (structural damage) and impairment (loss of function). It is a syndrome that rarely has a sole and distinct pathophysiology. Many patients with AKI have a mixed aetiology where the presence of sepsis, ischaemia, and nephrotoxicity often co-exist and complicate recognition and treatment. Furthermore, the syndrome is quite common among patients without critical illness, and it is essential that health care professionals, particularly those without specialisation in renal disorders, detect it easily.

Classification of AKI includes pre-renal AKI, acute post-renal obstructive nephropathy, and intrinsic acute kidney diseases. Of these, only ‘intrinsic’ AKI represents true kidney disease, while pre-renal and post-renal AKI are the consequence of extra-renal diseases leading to the decreased glomerular filtration rate (GFR). If these pre- and/or post-renal conditions persist, they will eventually evolve to renal cellular damage and hence intrinsic renal disease. (Ref https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5198510/)

Chronic Kidney Failure (CRF):-
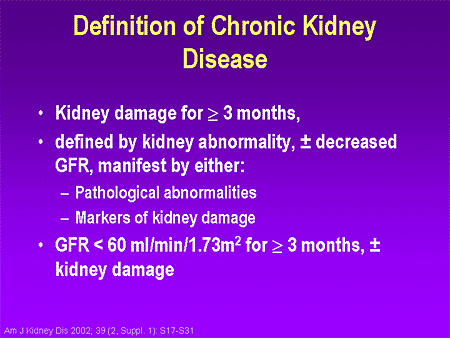
A patient is said to have chronic kidney disease (CKD) if they have abnormalities of kidney function or structure present for more than 3 months. The definition of CKD includes all individuals with markers of kidney damage or those with an eGFR of less than 60 ml/min/1.73m2 on at least 2 occasions, 90 days apart (with or without markers of kidney damage).
Causes of chronic renal failure:-
Ayurvedic View :
The kidneys are mentioned as vrikka in Ayurveda. Shotha is the name for swelling. Some books in Ayurveda have mentioned vrikka vicar (kidney disorders) separately, while many have elaborately described the shotha vicar, its types, and effective methods to manage them.
Causes according to Ayurveda :
According to Ayurveda, urine formation starts in the intestine itself, although filtration takes place in the kidneys. An imbalance of agni (fire element ) disturbs the process of formation and filtration of urine. Malformed urine leads to the accumulation of wastes in the body. This unwanted accumulation is known as ‘ama sanchaya’ (toxin accumulation) in Ayurveda. This ‘ama’ accumulation manifests as loss of appetite, tiredness, heaviness, puffiness around the eyes, excess water in the later stages, and abnormal values of Creatinine, Urea, GFR, e.t.c. On the basis of different factors, damage at different levels of the filtration apparatus can take place.
So, Chronic kidney disease is a condition of the mutravaha srotas (The body channel that is related to the urinary system of the body and its normal functioning). The damage to the tissues is contributed by the imbalance in the three doshas (body humors - Air, Fire, and Ether/ Vata, Pitta, and Kapha), mainly the vitiated Vata element and the raised Kapha element, which leads to the blockage of various channels of the Mutra vaha srotasa, leading to impaired functioning of the kidneys.
Ayurvedic Herbal Treatment options :
The Ayurvedic treatment of chronic renal failure is based on three principles:
(i) Helping the damaged kidneys - The damage done to the kidneys can be managed using herbal combinations like Punarnavadi Guggulu, Gokshuradi Guggulu, Gomutra Haritaki, Chandraprabha Vati, and Punarnavadi Qadha (decoction). Herbal medicines useful in this condition are: Punarnava (Boerhaavia diffusa), Gokshur (Tribulus terrestris), Haritaki (Terminalia chebula), Neem (Azadirachta indica), Daruharidra (Berberis aristata), and Patol (Tricosanthe dioica).

(ii) Treating the body tissues (dhatus) which make up the kidneys - According to Ayurveda, the kidneys are made up of the "Rakta" and "Meda" dhatus. Treating these two dhatus is also an effective way to help the kidneys. Herbs used are: Patol, Saariva, Patha (Cissampelos pareira), Musta (Cyperus rotundus), Kutki (Picrorrhiza kurroa), Chirayta (Swertia chirata), Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia), Chandan (Santalum album), and Shunthi (Zinziber officinalis).
(iii) Treating the known cause - Ayurvedic herbal remedies are especially useful in treating renal causes resulting in acute organ failure, which include diseases like glomerulonephritis, acute interstitial nephritis, and acute tubular necrosis. Herbal combinations like Chandraprabha-Vati, Gokshuradi-Guggulu, Maha-Manjishthadi-Qadha, Saarivasav, Chandrakala-Ras, Sutshekhar-Ras, Punarnavadi-Guggulu, Punarnavadi-Qadha, Shankh-Vati, Panchamrut-Parpati, Yava-Kshar, and Surya-Kshar are very effective in managing these conditions. Primary glomerular diseases like membranous nephropathy and glomerulonephritis can be managed using Punarnava, Gokshur, Saariva, and Manjishtha. Secondary glomerular disease resulting from diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, etc., can be treated accordingly, using the medicines appropriate for those diseases. Similarly, suitable Ayurvedic remedies can be given for other causes like polycystic kidneys, prostate enlargement, and neurogenic bladder.
General Tips :
Disclaimer : Sandeep Kumar and Anupam Vasudeva are not GP, they have Ayurveda medical degree from India where it is considered equal to any other medical degree. This qualification is recognized in Australia by vetassess governing body as Complementary Health Therapists. Life Line Ayurvedic Herbal Clinic does not claim to cure a disease or terminal illness and does not create any unreasonable expectation of beneficial treatment. Ayurvedic medicines and treatments are generally considered to be safe but rarely may be associated with possible adverse reactions in individual cases. We recommend seeking urgent medical attention in the case of an adverse reaction. This website provides you with information. You must contact your Ayurvedic or another health professional before you apply them. Read More